In today’s globalized economy, the movement of temperature-sensitive products such as pharmaceuticals, fresh food, dairy, seafood, frozen items, and biological materials has increased significantly. Ensuring that these products remain within a specified temperature range from origin to destination is critical for maintaining their quality, safety, and effectiveness. This entire process is known as the cold chain.
A cold chain is more than just refrigeration—it is a carefully managed system of people, equipment, processes, and technologies working together to preserve product integrity. Any break in this chain can result in spoilage, financial losses, regulatory penalties, and even serious health risks.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the key components of cold chain and explain their importance in temperature-controlled transportation, while also highlighting best practices, challenges, and future trends in cold chain logistics.
What Is Cold Chain?
The cold chain refers to a temperature-controlled supply chain that includes storage, handling, transportation, and monitoring of perishable goods. It ensures that products remain within a defined temperature range from production to final consumption.
Cold chain logistics is essential for:
- Food and beverage industry
- Pharmaceutical and healthcare sector
- Biotechnology and vaccines
- Chemical and specialty products
- Floral and horticulture industry
Without a well-maintained cold chain system, even high-quality products can quickly degrade.

Why Cold Chain Is Crucial in Temperature-Controlled Transportation
Temperature-controlled transportation is the backbone of cold chain logistics. It allows products to move safely over long distances without compromising quality.
Key benefits include:
- Prevention of spoilage and contamination
- Compliance with regulatory standards
- Extended shelf life of products
- Reduced product waste
- Improved customer satisfaction
Maintaining consistent temperature during transit is essential to protect product value and brand reputation.
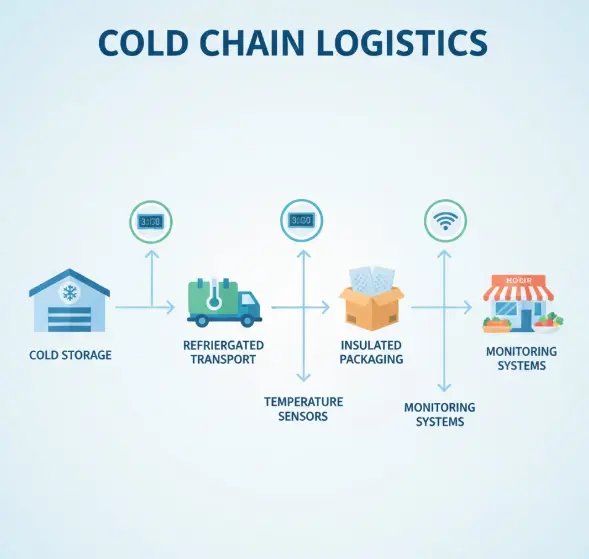
Key Components of Cold Chain
Let’s break down the major components that make up a successful cold chain system.
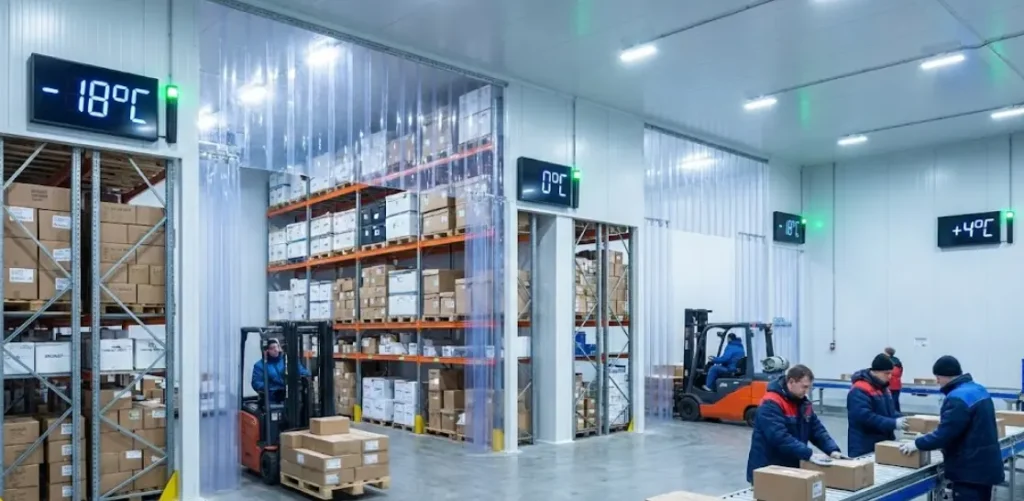
1. Temperature-Controlled Storage Facilities
Cold storage facilities form the foundation of the cold chain. These warehouses are designed to maintain specific temperature zones such as:
- Chilled storage (0°C to 5°C)
- Frozen storage (-18°C and below)
- Deep frozen storage (-30°C or lower)
These facilities use advanced insulation, refrigeration systems, and backup power solutions to maintain stable conditions.
Importance:
- Preserves product quality before dispatch
- Enables bulk storage for large volumes
- Supports inventory management and order fulfillment
2. Refrigeration Equipment
Refrigeration equipment includes chillers, freezers, blast freezers, and refrigeration units installed in warehouses and vehicles.
Key features:
- Precise temperature control
- Energy-efficient compressors
- Digital temperature displays
- Alarm systems for temperature deviations
Importance:
- Maintains consistent cooling
- Prevents temperature fluctuations
- Ensures compliance with storage requirements
3. Refrigerated Transportation (Reefer Vehicles)
Refrigerated trucks, vans, containers, and trailers are essential for moving perishable goods between facilities and final destinations.
Types of temperature-controlled vehicles:
- Single-compartment refrigerated trucks
- Multi-temperature zone trucks
- Refrigerated containers for sea freight
- Insulated delivery vans
Importance:
- Protects products during transit
- Enables long-distance distribution
- Supports just-in-time delivery
4. Packaging Solutions
Cold chain packaging is designed to maintain temperature and protect products from physical damage.
Common packaging materials include:
- Insulated boxes
- Gel packs and ice packs
- Vacuum-insulated panels
- Phase change materials
Importance:
- Adds an extra layer of temperature protection
- Reduces risk of thermal shock
- Ensures product stability during handling
5. Temperature Monitoring Systems
Monitoring systems track temperature and humidity throughout storage and transportation.
Examples:
- Data loggers
- Wireless temperature sensors
- GPS-enabled tracking devices
- Cloud-based monitoring platforms
Importance:
- Provides real-time visibility
- Helps identify temperature excursions
- Enables corrective actions
6. Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
SOPs define how products should be handled at every stage of the cold chain.
They include:
- Loading and unloading procedures
- Cleaning and sanitation protocols
- Temperature set-point guidelines
- Emergency response plans
Importance:
- Ensures consistency
- Reduces human error
- Supports regulatory compliance
7. Skilled Workforce
Trained personnel are critical to cold chain success.
Key roles:
- Warehouse operators
- Quality control staff
- Drivers and logistics coordinators
- Cold chain technicians
Importance:
- Proper handling of products
- Accurate documentation
- Rapid response to issues
8. Quality Control and Compliance
Quality assurance ensures adherence to food safety and pharmaceutical regulations.
Activities include:
- Regular audits
- Equipment calibration
- Documentation and record-keeping
- Validation of storage and transport conditions
Importance:
- Builds trust with customers
- Prevents legal issues
- Ensures product safety
9. Information Technology Systems
IT systems integrate all cold chain operations.
Examples:
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
- Transportation Management Systems (TMS)
- Inventory tracking software
- Analytics dashboards
Importance:
- Improves operational efficiency
- Enhances traceability
- Supports data-driven decisions
10. Risk Management and Contingency Planning
Unexpected events such as power failures, vehicle breakdowns, or natural disasters can disrupt the cold chain.
Risk mitigation measures:
- Backup generators
- Alternative transport routes
- Emergency cold storage access
- Insurance coverage
Importance:
- Minimizes downtime
- Reduces losses
- Ensures business continuity
Importance of Cold Chain in Different Industries
Food and Beverage Industry
Cold chain prevents spoilage and preserves taste, texture, and nutritional value. It also reduces food waste and improves shelf life.
Pharmaceutical and Healthcare Sector
Vaccines, insulin, and biological products require strict temperature control. Even minor deviations can render them ineffective.
Agriculture and Horticulture
Fresh fruits, vegetables, and flowers require specific temperatures to remain fresh during export and domestic distribution.
Chemicals and Specialty Products
Certain chemicals and industrial materials are sensitive to temperature and require controlled environments.
Challenges in Cold Chain Management
Despite technological advancements, cold chain logistics faces several challenges:
- High operational costs
- Energy consumption
- Infrastructure gaps in remote areas
- Temperature fluctuations during handling
- Lack of skilled professionals
Addressing these challenges requires investment, training, and adoption of modern technology.
Best Practices for Effective Cold Chain Management
- Conduct regular equipment maintenance
- Use real-time temperature monitoring
- Train staff periodically
- Implement standardized procedures
- Perform audits and inspections
- Partner with reliable logistics providers
These practices help maintain a strong and reliable cold chain.
Future Trends in Cold Chain Logistics
The cold chain industry is evolving rapidly. Emerging trends include:
- IoT-enabled sensors
- Artificial intelligence for predictive maintenance
- Automation in cold storage warehouses
- Sustainable refrigeration technologies
- Blockchain for traceability
These innovations will improve efficiency, transparency, and sustainability.
Conclusion
The Cold Chain Transportation is a complex yet essential system that ensures temperature-sensitive products reach consumers safely and in perfect condition. From cold storage facilities and refrigeration equipment to monitoring systems and trained personnel, every component plays a vital role.
Understanding the key components of cold chain and their importance in temperature-controlled transportation helps businesses build reliable supply chains, reduce losses, and meet customer expectations. As global demand for perishable goods continues to grow, investing in robust cold chain infrastructure is no longer optional—it is a necessity.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the most important component of the cold chain?
All components are important, but temperature monitoring systems are critical because they ensure visibility and control across the entire chain.
Q2. What temperature ranges are commonly used in cold chain logistics?
Chilled (0°C to 5°C), frozen (-18°C), and deep frozen (-30°C or below).
Q3. How does cold chain reduce product waste?
By maintaining consistent temperature, products remain fresh longer, reducing spoilage and losses.
Q4. Why is packaging important in cold chain?
Packaging provides insulation and protects products from temperature fluctuations during transit.
Q5. What industries benefit most from cold chain logistics?
Food, pharmaceuticals, healthcare, agriculture, biotechnology, and chemicals.




